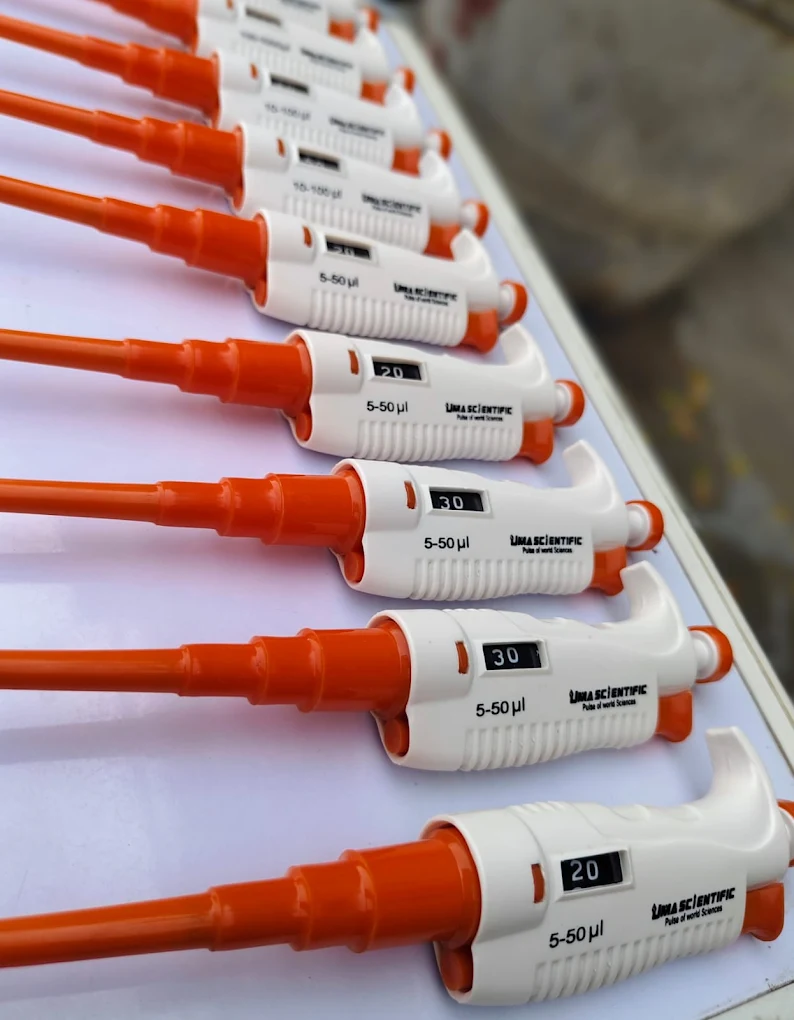
Introduction to Micropipettes
Micropipettes are precision instruments widely used in laboratories to measure and transfer small volumes of liquid, typically in the microliter range (0.1 µL to 1000 µL). These devices are indispensable in scientific research, enabling accurate and reproducible results in fields such as molecular biology, microbiology, biochemistry, and clinical diagnostics. At Uma Scientific, we understand the critical role micropipettes play in ensuring experimental success across laboratories in India, from bustling metropolitan cities like Mumbai and Delhi to emerging research hubs in smaller states like Mizoram and Nagaland.
This SEO-friendly blog post provides a detailed exploration of micropipettes, including their working principles, types, and applications, while highlighting their significance in laboratories across all Indian states. Whether you’re a researcher in Tamil Nadu, a student in Uttar Pradesh, or a lab technician in Assam, this guide will help you understand micropipettes and their essential role in scientific advancement.
What is a Micropipette?
A micropipette is a sophisticated laboratory tool designed to dispense precise volumes of liquid, often as small as 0.1 microliters. Unlike traditional pipettes, which handle larger volumes, micropipettes are engineered for accuracy in handling minute quantities, making them vital for experiments where precision is paramount. They are commonly used in DNA amplification, enzyme assays, and clinical testing, ensuring consistent and reliable results.
Micropipettes are equipped with a piston mechanism that allows for the aspiration and dispensing of liquids through disposable tips, minimizing contamination risks. Their ergonomic design and precise calibration make them user-friendly and efficient, catering to the needs of laboratories in states like Karnataka, West Bengal, and Gujarat.
Working Principle of Micropipettes
Micropipettes operate on two primary mechanisms: air displacement and positive displacement. Each mechanism is suited to specific applications, depending on the nature of the liquid being handled.
Air Displacement Micropipettes
The air displacement mechanism is the most common type used in laboratories across India, from research facilities in Hyderabad, Telangana, to academic institutions in Jaipur, Rajasthan. This type relies on a piston that moves within a cylinder to create a vacuum. Here’s how it works:
- Aspiration: When the plunger is pressed and released, a vacuum is created inside the micropipette, drawing liquid into a disposable tip. The air cushion between the piston and the liquid ensures no direct contact, reducing contamination risks.
- Dispensing: Pressing the plunger again expels the liquid from the tip into the target container. The air displacement method is ideal for aqueous solutions and is widely used in labs in states like Kerala, Punjab, and Odisha.
Positive Displacement Micropipettes
Positive displacement micropipettes are designed for handling viscous, volatile, or dense liquids, such as those used in specialized experiments in Andhra Pradesh or Chhattisgarh. In this mechanism:
- Direct Contact: The piston directly contacts the liquid through a disposable microsyringe tip, eliminating the air cushion. This ensures precise transfer of challenging liquids like oils or high-viscosity reagents.
- Applications: This type is preferred for applications requiring high accuracy with non-aqueous samples, such as in pharmaceutical labs in Maharashtra or forensic labs in Bihar.
Both mechanisms ensure precision, but the choice depends on the liquid properties and experimental requirements. Laboratories in states like Jharkhand, Uttarakhand, and Himachal Pradesh rely on these mechanisms for diverse applications.
Types of Micropipettes
Micropipettes come in various types, each tailored to specific laboratory needs. Below are the main categories available at Uma Scientific, serving researchers across India, from Arunachal Pradesh to Goa.
1. Single-Channel Micropipettes
Single-channel micropipettes are the most common, used for transferring a single liquid sample at a time. They are ideal for applications in molecular biology and microbiology labs in cities like Chennai, Tamil Nadu, or Lucknow, Uttar Pradesh. Key features include:
- Volume Range: Typically 0.1 µL to 1000 µL.
- Applications: Used in DNA sequencing, PCR, and cell culture experiments in labs across Madhya Pradesh and Haryana.
- Advantages: Cost-effective, easy to use, and suitable for general-purpose liquid handling.
2. Multi-Channel Micropipettes
Multi-channel micropipettes, with 8, 12, or 16 channels, allow simultaneous transfer of multiple samples. They are perfect for high-throughput experiments in states like Andhra Pradesh and Karnataka. Features include:
- Efficiency: Ideal for filling 96-well plates in ELISA or molecular screening, common in research centers in Gujarat and Rajasthan.
- Ergonomics: Reduces operator workload, especially in large-scale labs in Delhi or West Bengal.
- Applications: Used in diagnostic testing and DNA amplification.
3. Fixed-Volume Micropipettes
Fixed-volume micropipettes dispense a predetermined volume, making them ideal for repetitive tasks in labs in Assam, Manipur, or Tripura. Benefits include:
- Accuracy: No need for volume adjustments, ensuring consistency.
- Applications: Suitable for routine assays with viscous liquids, such as in clinical labs in Sikkim or Meghalaya.
4. Variable-Volume Micropipettes
Variable-volume micropipettes allow users to adjust the volume within a specific range, offering flexibility for labs in states like Odisha, Jharkhand, and Chhattisgarh. Key points:
- Versatility: Adjustable volumes cater to diverse experiments.
- Applications: Used in analytical chemistry and biochemistry in research facilities across Telangana and Uttarakhand.
5. Electronic Micropipettes
Electronic micropipettes, available in single or multi-channel variants, use a battery-powered motor to automate liquid handling, reducing user fatigue in labs in Himachal Pradesh or Nagaland. Features include:
- Precision: Enhanced accuracy with digital controls.
- Programmability: Custom programs for specific protocols, popular in high-tech labs in Bangalore, Karnataka.
- Applications: Ideal for high-throughput experiments like kinetic studies and ELISA in Maharashtra or Punjab.
6. Specialty Micropipettes
Specialty micropipettes, such as glass-tipped or ultra-macro pipettes, cater to niche applications in states like Mizoram, Arunachal Pradesh, and Goa. Examples include:
- Van Slyke Pipettes: Used for gas analysis in environmental labs.
- Microfluidic Pipettes: For precise handling in advanced biotechnology research.
- High-Volume Pipettes: Capable of dispensing up to 50 mL, used in industrial labs in Gujarat or Tamil Nadu.
Uses of Micropipettes Across India
Micropipettes are versatile tools with applications spanning multiple disciplines. Below are key uses in laboratories across all Indian states:
1. Molecular Biology
In molecular biology labs in cities like Pune, Maharashtra, or Kolkata, West Bengal, micropipettes are essential for:
- DNA and RNA Extraction: Precise handling of nucleic acids for sequencing and amplification.
- PCR (Polymerase Chain Reaction): Accurate dispensing of reagents for genetic research in labs in Delhi and Hyderabad.
- Cloning and Gene Editing: Ensuring precise volumes for CRISPR and other techniques in Tamil Nadu and Karnataka.
2. Microbiology
Microbiology labs in states like Uttar Pradesh, Bihar, and Assam rely on micropipettes for:
- Culture Preparation: Transferring microbial samples for growth studies.
- Antibiotic Sensitivity Testing: Dispensing precise volumes for accurate results.
- Environmental Testing: Analyzing water and soil samples in labs in Jharkhand and Odisha.
3. Clinical Diagnostics
Clinical labs across India, from Rajasthan to Kerala, use micropipettes for:
- Blood and Serum Analysis: Measuring small volumes for diagnostic assays.
- ELISA Testing: Handling samples for antibody detection in labs in Punjab and Haryana.
- Pathogen Detection: Supporting rapid diagnostics in hospitals in Manipur and Tripura.
4. Biochemistry and Analytical Chemistry
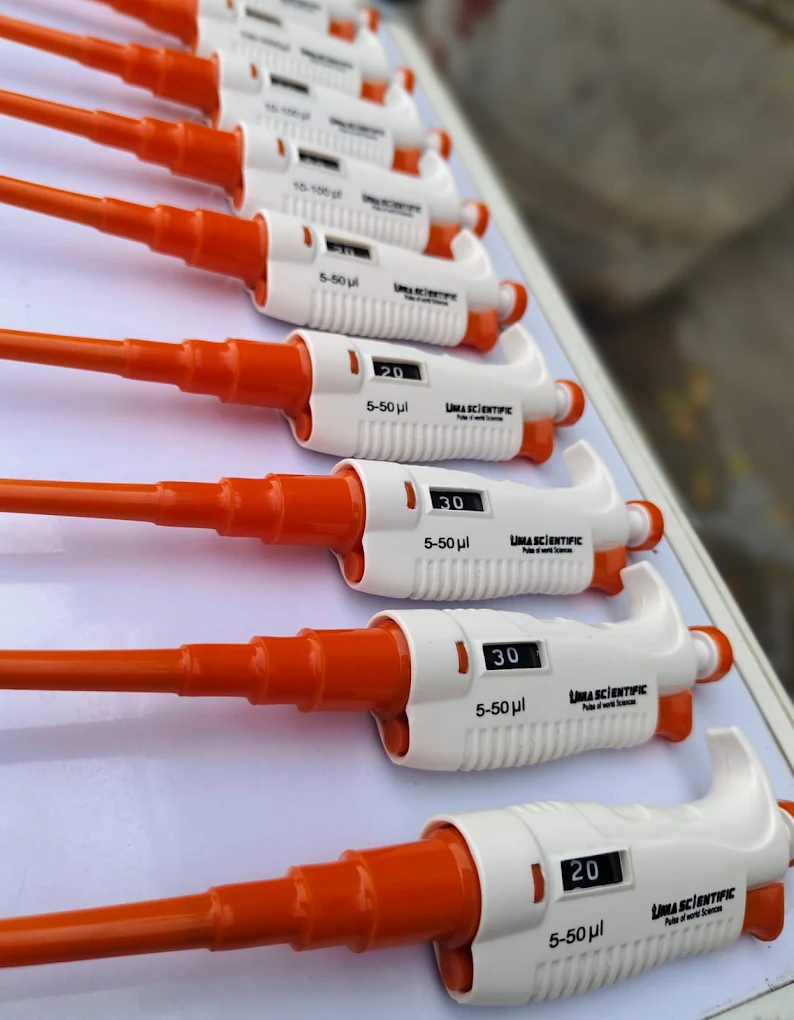

In biochemistry labs in states like Gujarat, Andhra Pradesh, and Chhattisgarh, micropipettes are used for:
- Enzyme Assays: Measuring reagents for kinetic studies.
- Protein Analysis: Handling samples for spectroscopy and chromatography.
- Quality Control: Ensuring accuracy in chemical analysis in industrial labs in Madhya Pradesh.
5. Pharmaceutical Research
Pharmaceutical labs in cities like Ahmedabad, Gujarat, or Chennai, Tamil Nadu, use micropipettes for:
- Drug Formulation: Measuring active ingredients with precision.
- High-Throughput Screening: Testing drug candidates in multi-channel setups.
- Quality Assurance: Ensuring consistency in drug development processes in Maharashtra and Karnataka.
6. Food Safety and Environmental Testing
Micropipettes play a crucial role in food safety labs in states like West Bengal, Odisha, and Sikkim for:
- Contaminant Detection: Analyzing food samples for pathogens or chemicals.
- Environmental Monitoring: Testing water and air samples for pollutants in labs in Uttarakhand and Himachal Pradesh.
- Soil Analysis: Measuring nutrient levels for agricultural research in Punjab and Haryana.
7. Academic and Research Institutions
Across India, from universities in Delhi to research institutes in Mizoram, micropipettes are used in:
- Student Training: Teaching precise liquid handling in labs in Uttar Pradesh and Rajasthan.
- Basic Research: Supporting experiments in biology, chemistry, and physics in states like Goa and Nagaland.
- Interdisciplinary Studies: Facilitating research in biotechnology and nanotechnology in Karnataka and Telangana.
Micropipette Usage Across Indian States
Micropipettes are integral to scientific progress in every Indian state, supporting research and diagnostics in diverse settings:
- Andhra Pradesh: Used in biotech hubs in Visakhapatnam for DNA research.
- Arunachal Pradesh: Supporting environmental studies in remote labs.
- Assam: Facilitating clinical diagnostics in Guwahati hospitals.
- Bihar: Used in agricultural research labs in Patna for soil testing.
- Chhattisgarh: Supporting industrial labs in Raipur for chemical analysis.
- Goa: Used in marine biology research for precise sample handling.
- Gujarat: Supporting pharmaceutical research in Ahmedabad.
- Haryana: Used in food safety labs in Gurugram.
- Himachal Pradesh: Facilitating environmental monitoring in Shimla.
- Jharkhand: Supporting microbiology labs in Ranchi.
- Karnataka: Used in high-tech biotech labs in Bangalore.
- Kerala: Supporting clinical diagnostics in Kochi.
- Madhya Pradesh: Used in industrial quality control in Bhopal.
- Maharashtra: Supporting pharmaceutical and molecular biology labs in Mumbai and Pune.
- Manipur: Used in clinical labs for pathogen detection.
- Meghalaya: Supporting environmental research in Shillong.
- Mizoram: Used in small-scale research labs for biotechnology.
- Nagaland: Facilitating academic research in Kohima.
- Odisha: Supporting marine and environmental labs in Bhubaneswar.
- Punjab: Used in agricultural and food safety labs in Ludhiana.
- Rajasthan: Supporting clinical and academic labs in Jaipur.
- Sikkim: Used in environmental testing labs in Gangtok.
- Tamil Nadu: Supporting biotech and clinical research in Chennai.
- Telangana: Used in advanced biotech labs in Hyderabad.
- Tripura: Supporting small-scale clinical labs in Agartala.
- Uttar Pradesh: Used in academic and clinical labs in Lucknow.
- Uttarakhand: Supporting environmental research in Dehradun.
- West Bengal: Used in molecular biology labs in Kolkata.
How to Use a Micropipette: Best Practices
Using a micropipette correctly ensures accuracy and prevents contamination. Follow these steps, widely practiced in labs across India:
- Select the Right Micropipette: Choose a micropipette based on the volume range needed, whether in a lab in Delhi or Kerala.
- Attach a Disposable Tip: Securely attach a compatible tip, ensuring no gaps, as practiced in labs in Gujarat and Tamil Nadu.
- Set the Volume: Adjust the volume dial to the desired setting for precise measurements in labs in Uttar Pradesh or Karnataka.
- Aspirate Liquid: Press the plunger to the first stop, insert the tip into the liquid, and slowly release the plunger to draw liquid, a common technique in Maharashtra and Rajasthan.
- Dispense Liquid: Place the tip in the target container, press the plunger to the second stop to dispense, and release, used in labs in Odisha and Punjab.
- Eject the Tip: Press the tip ejector to safely remove the tip, preventing contamination in labs in Assam or West Bengal.
- Clean and Store: Clean the micropipette with 70% ethanol and store vertically in a stand, as done in labs in Himachal Pradesh and Telangana.
Maintenance and Calibration
Regular maintenance and calibration are crucial for micropipette accuracy, especially in high-precision labs in states like Andhra Pradesh and Haryana. Key tips include:
- Cleaning: Use a lint-free cloth with mild detergent or 70% ethanol to clean the exterior. For internal cleaning, disassemble and clean parts as recommended in labs in Madhya Pradesh.
- Calibration: Regularly calibrate micropipettes to ensure accuracy, a standard practice in research facilities in Karnataka and Maharashtra.
- Storage: Store vertically to prevent liquid ingress, as practiced in labs in Sikkim and Mizoram.
SEO-Friendly Tips for Writing About Micropipettes
To ensure this blog post is SEO-friendly and reaches researchers across India, we’ve incorporated best practices:
- Keyword Optimization: Used keywords like “micropipette working principle,” “types of micropipettes,” and “micropipette uses in India” naturally throughout the text.
- Search Intent: Addressed informational intent by providing a comprehensive guide for researchers, students, and lab technicians in states like Uttar Pradesh, Tamil Nadu, and Gujarat.
- Readability: Used clear headings, bullet points, and concise language to enhance user experience, as recommended for labs in Delhi and West Bengal.
- Internal Linking: Referenced related topics like “micropipette maintenance” and “laboratory equipment in India” to guide users to additional resources.
- Local Relevance: Included all Indian states to cater to location-specific searches, ensuring visibility in cities like Mumbai, Bangalore, and smaller regions like Nagaland and Tripura.
Conclusion
Micropipettes are indispensable tools in modern laboratories, enabling precise liquid handling for groundbreaking research and diagnostics across India. From the air displacement micropipettes used in molecular biology labs in Hyderabad to positive displacement models in pharmaceutical labs in Ahmedabad, these instruments drive scientific progress. At Uma Scientific, we are committed to providing high-quality micropipettes to support researchers in every state, from Arunachal Pradesh to West Bengal.
Whether you’re conducting DNA amplification in Tamil Nadu, clinical diagnostics in Kerala, or environmental testing in Himachal Pradesh, understanding the working principles, types, and uses of micropipettes is essential for success. By following best practices and maintaining these precision instruments, laboratories across India can achieve accurate and reproducible results, advancing science and innovation nationwide.
For more information about our micropipettes or to explore our range of laboratory solutions, contact Uma Scientific at sales.umascientific@gmail.com or call +91 7379207507 or +91 7347707507. Let us help you elevate your research with precision and reliability.