When it comes to handling liquids in a laboratory setting, precision is everything. Whether you’re conducting chemical experiments, biological assays, or medical diagnostics, accurate liquid measurement and transfer is crucial. However, the terms pipet, pipette, and micropipette often cause confusion. Are they the same? Is there any difference? And if so, which one should you use for your specific application?
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll break down these terms, explore their differences, and explain the best uses for each type of liquid handling tool.
What Is a Pipet?
The word pipet (or pipette, depending on spelling preference) generally refers to a laboratory tool used to transport a measured volume of liquid. The term “pipet” is more commonly used in American English, while “pipette” is the preferred spelling in British English. But both words essentially describe the same tool.

Types of Pipets
Pipets come in several varieties, but they broadly fall into two categories:
- Volumetric pipets: These are designed to measure a single, precise volume of liquid with high accuracy. For example, a 10 mL volumetric pipet can only measure exactly 10 mL.
- Graduated pipets: These pipets have volume markings along the length, allowing for measurement of variable volumes. However, they are less precise than volumetric pipets.
Typical Usage
Pipets are typically glass or plastic tubes used in chemistry and biology labs to transfer volumes from a few milliliters up to about 50 mL. They are used for tasks like preparing solutions, titrations, and sample dilution.
What Is a Pipette?
Pipette is just an alternative spelling of pipet, but it is often used more specifically in certain contexts, especially in molecular biology and biochemistry. The spelling difference doesn’t imply a difference in function, but “pipette” has become synonymous with more modern, precision tools.
Modern Pipettes
Modern pipettes come in various sophisticated types:
- Manual pipettes: These include single-channel and multi-channel pipettes, often used in biological research.
- Electronic pipettes: Equipped with digital controls for volume selection and liquid dispensing.
- Micropipettes: Specialized pipettes designed for very small volumes (typically less than 1 mL).
What Is a Micropipette?
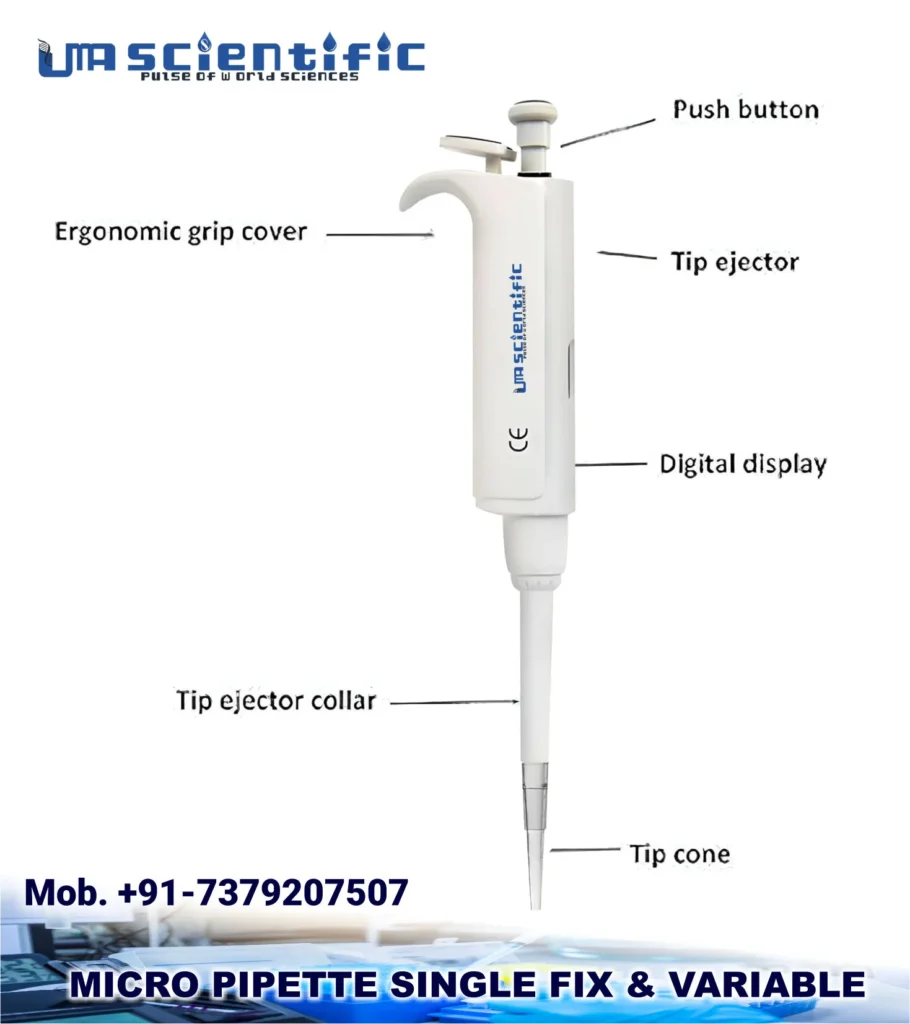
A micropipette is a specialized type of pipette designed for very precise measurement and transfer of extremely small liquid volumes, usually in the microliter (μL) range, which is one-thousandth of a milliliter.
Features of Micropipettes
- Volume range: Commonly from 0.1 μL to 1000 μL, with some models extending up to 10,000 μL (10 mL).
- Fixed-volume vs variable-volume: Fixed-volume micropipettes dispense a set volume, while variable-volume models allow adjustment within a range.
- Ergonomics: Micropipettes have ergonomic designs to reduce hand strain during repetitive use.
- Calibration: They require regular calibration to maintain accuracy, often adhering to ISO standards like ISO 8655.
- Autoclavable parts: For sterility, many micropipettes have parts that can be autoclaved.
Why Use a Micropipette?
Micropipettes are essential in fields like:
- Molecular biology (e.g., PCR, DNA sequencing)
- Clinical diagnostics (e.g., ELISA)
- Microbiology (e.g., bacterial cultures)
- Analytical chemistry (e.g., chromatography sample prep)
Their precision is critical when working with minute volumes where even slight inaccuracies could compromise results.
Key Differences Between Pipet, Pipette, and Micropipette
| Feature | Pipet/Pipette (General) | Micropipette |
|---|---|---|
| Volume Range | 1 mL to 50 mL (milliliters) | 0.1 μL to 1000 μL or more (microliters) |
| Accuracy | Moderate (depends on type) | High precision (ISO calibrated) |
| Material | Usually glass or plastic | Plastic with precision mechanics |
| Usage | General liquid transfer and measurement | Precise small-volume applications |
| Operation | Manual, gravity or suction-based | Manual or electronic piston-driven |
| Calibration Needed | Sometimes, less frequently | Regular, mandatory |
| Ergonomics | Basic | Ergonomic for repetitive use |
| Cost | Usually low to moderate | Moderate to high |
When to Use Each?
Use a Pipet/Pipette When:
- Handling relatively large volumes (1 mL or more)
- Performing general lab tasks like solution preparation
- You need a cost-effective, simple tool
- Precision at microliter scale is not critical
Use a Micropipette When:
- Working with very small volumes (< 1 mL)
- Accuracy and reproducibility are critical
- Performing molecular biology, diagnostics, or analytical chemistry
- You need ergonomic and user-friendly tools for repetitive use
How to Properly Use a Micropipette
Proper technique ensures accuracy and longevity of micropipettes:
- Select the correct volume range on the micropipette.
- Attach a compatible disposable tip securely.
- Press the plunger to the first stop before immersing the tip in liquid.
- Immerse the tip just below the liquid surface to avoid air bubbles.
- Slowly release the plunger to aspirate liquid.
- Dispense liquid by pressing the plunger to the second stop fully.
- Eject the tip after use to avoid contamination.
- Calibrate and clean regularly for optimal performance.
Maintaining Your Micropipette
- Store upright in a stand to avoid damage.
- Clean exterior with 70% ethanol regularly.
- Autoclave autoclavable parts as recommended.
- Avoid dropping or rough handling.
- Perform calibration every 6–12 months depending on usage.
Conclusion: Clarifying the Confusion
In summary:
- Pipet and pipette are essentially the same, differing mainly in spelling and minor usage preferences.
- Both terms refer to tools for liquid handling in the milliliter range.
- Micropipettes are advanced pipettes designed for small-volume precision work in the microliter range.
- Choosing the right tool depends on the volume you need to handle, the accuracy required, and your specific laboratory application.
Understanding these differences helps scientists, students, and lab professionals select the best liquid handling instrument for their needs — ensuring accuracy, efficiency, and successful experimental outcomes.
Contact us +917347707507 / +917379207507
pipet, pipette, micropipette, pipet vs pipette, pipette vs micropipette, micropipette uses, types of pipettes, laboratory pipettes, pipetting techniques, pipet accuracy, micropipette calibration, fixed volume pipette, variable volume pipette, multi-channel pipette, electronic pipette, manual pipette, micropipette volume range, lab equipment, liquid handling tools, pipette brands, pipette maintenance, pipetting errors, micropipette tips, micropipette manufacturer, pipette price India, micropipette India, scientific pipettes, biology lab tools, chemistry pipettes, micropipette applications, pipetting precision, lab instruments, micropipette for PCR, pipetting methods, disposable pipette tips, micropipette ergonomics, micropipette calibration standards, lab micropipette uses, micropipette vs serological pipette, micropipette cleaning, micropipette accuracy standards, micropipette features, micropipette suppliers India, pipette training, micropipette technology, pipette volume adjustment, micropipette repair, micropipette types explained, laboratory liquid measurement, micropipette advantages.