Micropipettes are essential tools in laboratories worldwide, enabling precise and accurate liquid handling for a wide range of scientific applications. Whether you’re a student stepping into a lab for the first time or a seasoned researcher, mastering the use of a micropipette is critical for achieving reliable experimental results. This 3000-word blog post provides a detailed, step-by-step guide on how to use a micropipette, covering types, techniques, maintenance, and best practices. By the end, you’ll have the knowledge and confidence to handle micropipettes like a pro.
What Is a Micropipette?
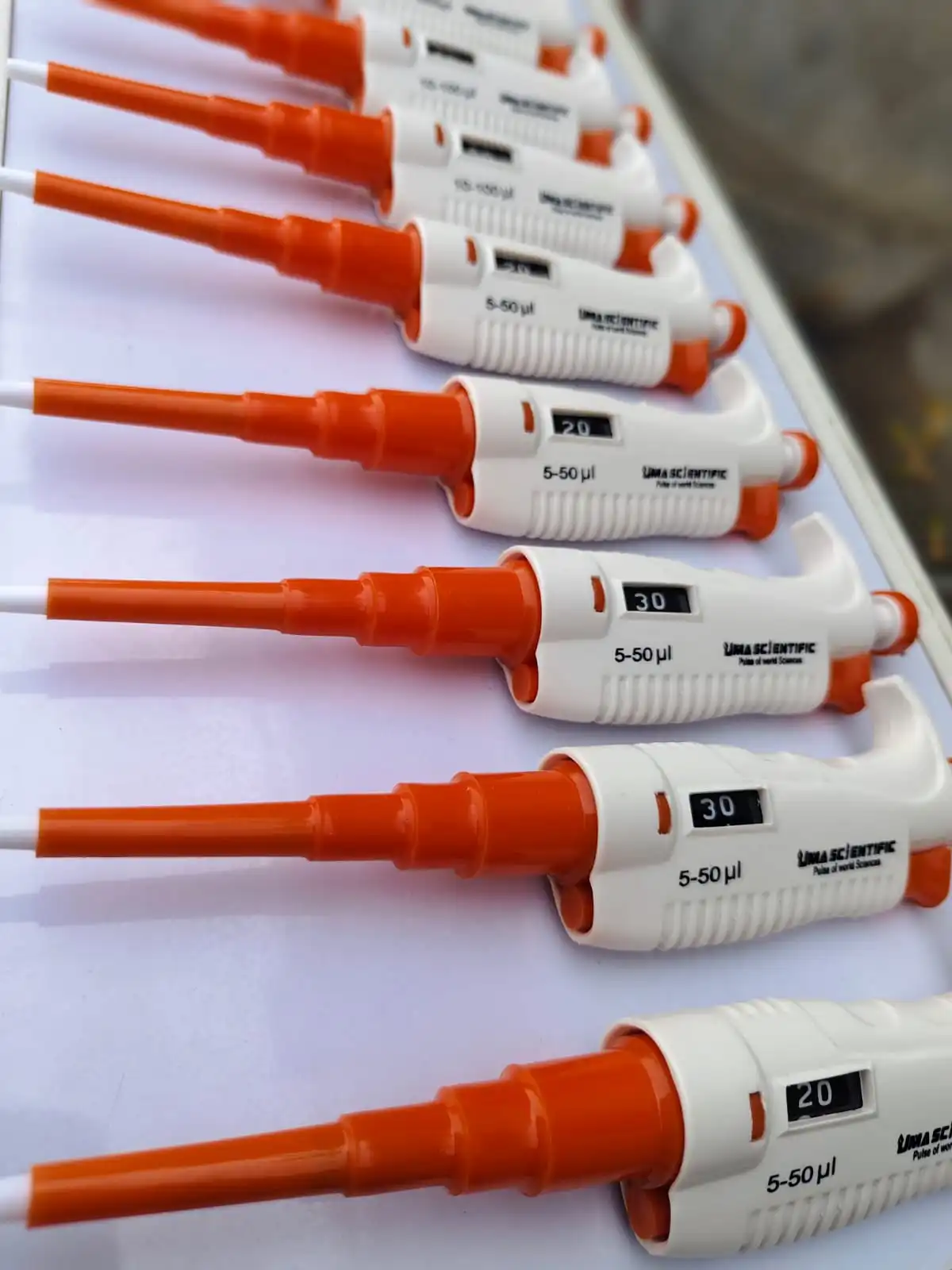
A micropipette is a precision instrument designed to measure and transfer small volumes of liquid, typically ranging from 0.1 μL to 10,000 μL (10 mL). Unlike larger-volume tools like graduated pipettes (5 mL, 10 mL, 25 mL, or 50 mL), micropipettes are used for applications requiring high accuracy, such as molecular biology, microbiology, biochemistry, and clinical diagnostics. They come in various types, including:

- Single-Channel Micropipettes: For transferring a single sample at a time.
- Multi-Channel Micropipettes: For simultaneous transfer of multiple samples (e.g., 8 or 12 channels).
- Fixed-Volume Micropipettes: Pre-set to dispense a specific volume.
- Variable-Volume Micropipettes: Allow adjustable volume settings.
- Electronic Micropipettes: Feature digital controls for enhanced precision and ease of use.
Micropipettes are equipped with a plunger, a volume adjustment mechanism, and a tip ejector, making them user-friendly and versatile. Brands like Uma Scientific and Labolit, leading manufacturers in India, offer high-quality micropipettes that meet global standards.
Why Learn to Use a Micropipette?
Proper use of a micropipette ensures:
- Accuracy and Precision: Critical for reproducible experimental results.
- Sample Integrity: Prevents contamination and sample loss.
- Efficiency: Saves time in high-throughput experiments.
- Safety: Reduces exposure to hazardous substances.
Whether you’re performing PCR, ELISA, or cell culture, mastering micropipette techniques is a fundamental lab skill. Let’s dive into the detailed process of using a micropipette.
Understanding Micropipette Components
Before using a micropipette, familiarize yourself with its key components:

- Plunger Button: Pressed to aspirate (draw up) and dispense liquid. Most micropipettes have two stops:
- First Stop: For aspirating and dispensing the set volume.
- Second Stop: For ejecting residual liquid during tip removal.
- Volume Adjustment Knob: Used to set the desired volume (on variable-volume models).
- Digital Display: Shows the selected volume (on variable-volume and electronic models).
- Tip Ejector Button: Releases the pipette tip without direct contact.
- Tip Cone: The part where disposable pipette tips are attached.
- Shaft: Connects the tip cone to the pipette body.
- Body/Handle: Ergonomically designed for comfortable grip.
Understanding these components helps you operate the micropipette correctly and avoid common errors.
Types of Micropipettes and Their Applications
Micropipettes are categorized based on their volume range and functionality. Common models include:
- P2/P10 (0.1–10 μL): For molecular biology tasks like PCR and DNA sequencing.
- P20 (2–20 μL): For small-volume assays and sample preparation.
- P100 (20–100 μL): For general lab work, such as enzyme assays.
- P200 (20–200 μL): For cell culture and biochemical experiments.
- P1000 (100–1000 μL): For larger volumes in microbiology and diagnostics.
- P5000/P10,000 (1–10 mL): For bulk liquid transfers.
Choose the appropriate micropipette based on your experiment’s volume requirements. For example, use a P10 for volumes below 10 μL and a P1000 for volumes above 100 μL.
Step-by-Step Guide to Using a Micropipette
Follow these steps to use a micropipette correctly:
Step 1: Select the Appropriate Micropipette
- Identify the volume you need to transfer (e.g., 5 μL, 50 μL, or 500 μL).
- Choose a micropipette with a range that covers your desired volume. For optimal accuracy, select a pipette where the target volume is within 10–100% of its maximum capacity. For example:
- For 5 μL, use a P10 (0.1–10 μL).
- For 50 μL, use a P100 (20–100 μL).
- For 500 μL, use a P1000 (100–1000 μL).
Step 2: Set the Volume (For Variable-Volume Micropipettes)
- Check the volume display to ensure it’s within the pipette’s range.
- Rotate the volume adjustment knob to set the desired volume:
- Turn clockwise to decrease the volume.
- Turn counterclockwise to increase the volume.
- Align the numbers on the digital display precisely. For example, to set 50 μL on a P100:
- The display might show “050.0” (50.0 μL).
- Avoid overshooting the pipette’s maximum or minimum volume to prevent damage.
Tip: If you overshoot the desired volume, dial back slightly below the target, then slowly increase to the correct setting to avoid mechanical backlash.

Step 3: Attach a Sterile Pipette Tip
- Select a compatible pipette tip for your micropipette model. Most brands, like Uma Scientific and Labolit, use universal tips.
- Open a box of sterile tips or use an autoclaved tip rack.
- Press the micropipette’s tip cone firmly into a tip until it clicks into place. Avoid touching the tip with your hands to prevent contamination.
- For multi-channel pipettes, ensure all channels have tips securely attached.
Note: Use filter tips for sensitive applications (e.g., PCR) to prevent aerosol contamination.
Step 4: Aspirate the Liquid
- Hold the micropipette vertically and grip it comfortably.
- Press the plunger smoothly to the first stop (do not press to the second stop yet).
- Immerse the pipette tip 2–3 mm into the liquid sample. Avoid submerging the tip too deeply to prevent liquid from entering the tip cone.
- Slowly release the plunger to aspirate the liquid. Allow the liquid to stabilize for 1–2 seconds.
- Lift the pipette straight out of the liquid to avoid touching the container’s sides.
Best Practice: For viscous liquids (e.g., glycerol), aspirate slowly and pause briefly to ensure complete uptake. For volatile liquids (e.g., ethanol), work quickly to minimize evaporation.
Step 5: Dispense the Liquid
- Position the pipette tip over the target container (e.g., a microcentrifuge tube or well plate).
- Angle the pipette at 10–45 degrees for optimal dispensing.
- Press the plunger smoothly to the first stop to dispense the liquid.
- Wait for 1–2 seconds to ensure all liquid is dispensed, especially for small volumes or viscous liquids.
- Press the plunger to the second stop to expel any residual liquid (this is called the “blow-out” step).
- Slowly release the plunger while keeping the tip in contact with the container’s wall to avoid splashing.
Tip: For multi-channel pipettes, ensure all tips are aligned with the wells of a plate to prevent uneven dispensing.
Step 6: Eject the Pipette Tip
- Hold the micropipette over a waste container or biohazard bin.
- Press the tip ejector button to release the tip. Avoid touching the used tip to prevent contamination.
- For multi-channel pipettes, ensure all tips are ejected simultaneously.
Safety Note: Dispose of used tips in a designated sharps or biohazard container, especially if they’ve contacted hazardous substances.

Step 7: Verify and Repeat
- Check the target container to ensure the correct volume was transferred.
- If performing multiple transfers, attach a new sterile tip and repeat the process.
- For repetitive dispensing, consider using an electronic micropipette with a multi-dispense mode to save time.
Common Micropipetting Techniques
Different applications require specific pipetting techniques to optimize accuracy and prevent errors:
- Forward Pipetting (Described Above):
- Standard method for aqueous solutions and non-viscous liquids.
- Press to first stop to aspirate, then to first stop to dispense, followed by blow-out.
- Reverse Pipetting:
- Ideal for viscous, volatile, or foamy liquids (e.g., glycerol, ethanol, or detergents).
- Press to second stop to aspirate, then to first stop to dispense (no blow-out).
- Retains residual liquid in the tip, which is discarded.
- Repetitive Pipetting:
- Used for dispensing multiple aliquots of the same volume.
- Aspirate a larger volume, then dispense smaller aliquots using the first stop.
- Common in multi-channel pipetting for plate-based assays.
- Mixing by Pipetting:
- After dispensing, aspirate and dispense the liquid repeatedly within the same container to mix.
- Use a fresh tip to avoid cross-contamination.
Best Practices for Micropipetting

To ensure accuracy, reproducibility, and safety, follow these best practices:
- Use the Correct Tip: Always use tips compatible with your micropipette model. Uma Scientific and Labolit offer universal tips for their pipettes.
- Maintain Vertical Alignment: Hold the pipette vertically during aspiration to prevent air bubbles.
- Avoid Overloading: Never set the volume beyond the pipette’s maximum or minimum range.
- Work at Room Temperature: Allow samples, pipettes, and tips to equilibrate to room temperature to minimize volume errors due to thermal expansion.
- Pre-Wet the Tip: For small volumes (<10 μL), aspirate and dispense the liquid once to coat the tip’s interior, improving accuracy.
- Minimize Air Exposure: Work quickly with volatile or sensitive samples to prevent evaporation or degradation.
- Calibrate Regularly: Ensure your micropipette is calibrated according to ISO 8655 standards (typically every 6–12 months).
- Avoid Contamination: Use sterile tips, wear gloves, and avoid touching the tip cone or sample container.
Maintenance and Care for Micropipettes
Proper maintenance extends the lifespan of your micropipette and ensures consistent performance:
- Cleaning:
- Wipe the exterior with 70% ethanol or a mild detergent.
- For autoclavable models, sterilize the tip cone at 121°C for 15–20 minutes (check the manufacturer’s guidelines).
- Avoid submerging the entire pipette in liquid.
- Calibration:
- Schedule professional calibration annually or as per your lab’s SOP.
- Perform in-house checks using a gravimetric method (weighing dispensed water on a precision balance).
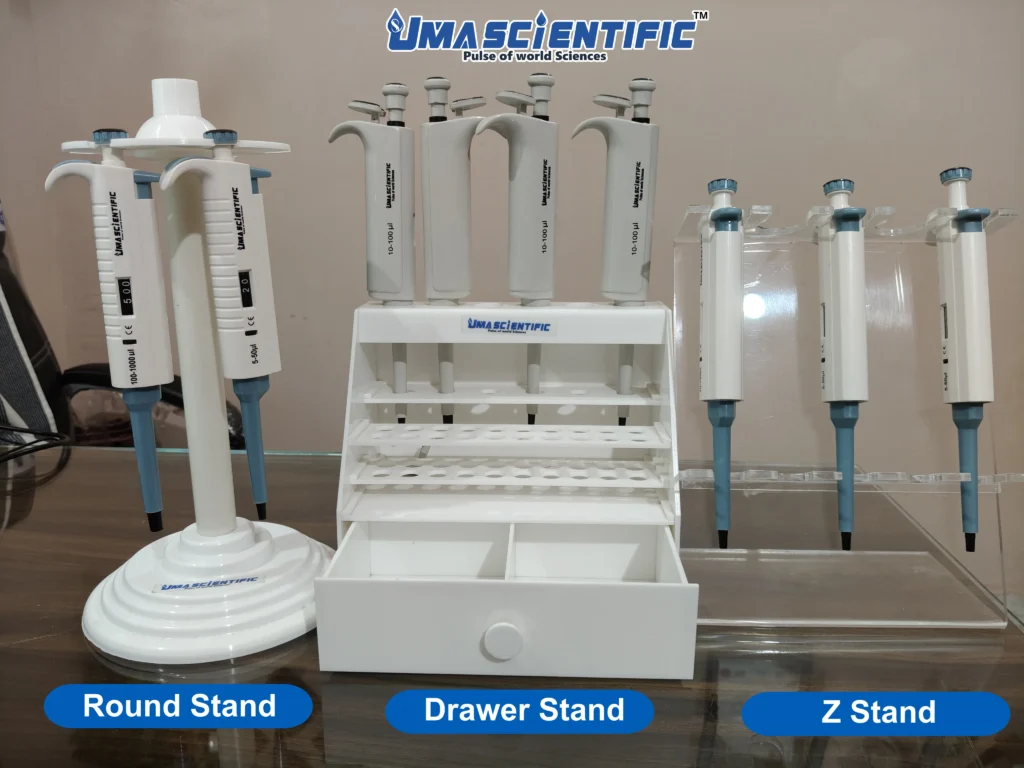
- Storage:
- Store micropipettes upright in a stand to prevent damage to the internal mechanism.
- Set variable-volume pipettes to their maximum volume to reduce spring tension.
- Inspection:
- Check for signs of wear, such as cracked tip cones or sticky plungers.
- Replace damaged parts promptly to maintain accuracy.
- Lubrication:
- Apply manufacturer-recommended lubricant to the piston periodically to ensure smooth operation.
- Avoid over-lubrication, which can attract dust and contaminants.
Note: Refer to the user manual for specific maintenance instructions. Brands like Uma Scientific and Labolit provide detailed guides with their products.
Troubleshooting Common Micropipette Issues
Even with proper technique, issues may arise. Here’s how to address them:
- Inaccurate Volumes:
- Cause: Incorrect volume setting, damaged tip cone, or miscalibration.
- Solution: Verify the volume, replace the tip cone, or recalibrate the pipette.
- Leaking Tips:
- Cause: Incompatible or damaged tips, or improper tip attachment.
- Solution: Use compatible tips and ensure a secure fit.
- Sticky Plunger:
- Cause: Dried residue or lack of lubrication.
- Solution: Clean and lubricate the piston as per the manufacturer’s instructions.
- Air Bubbles in Tip:
- Cause: Improper aspiration technique or low sample volume.
- Solution: Immerse the tip deeper and aspirate slowly.
- Contamination:
- Cause: Reusing tips or touching the tip cone.
- Solution: Use fresh sterile tips and handle the pipette carefully.
For persistent issues, contact the manufacturer’s customer support. Uma Scientific and Labolit offer reliable assistance at +91 7347707507.
Safety Considerations When Using Micropipettes
Micropipettes are safe when used correctly, but improper handling can pose risks:
- Chemical Exposure: Wear gloves, lab coats, and safety goggles when handling hazardous liquids.
- Biohazards: Use filter tips and dispose of tips in biohazard bins for biological samples.
- Ergonomic Strain: Use ergonomic pipettes and take breaks to prevent repetitive strain injuries.
- Cross-Contamination: Never reuse tips or aspirate from contaminated samples.
Applications of Micropipettes in Research and Industry
Micropipettes are versatile tools used in various fields:
- Molecular Biology: For DNA/RNA extraction, PCR, and sequencing.
- Microbiology: For bacterial culture and antibiotic sensitivity testing.
- Biochemistry: For protein quantification and enzyme kinetics.
- Clinical Diagnostics: For ELISA, blood analysis, and serological tests.
- Pharmaceuticals: For drug formulation and quality control.
- Environmental Science: For water and soil sample analysis.
Their precision and reliability make them indispensable in advancing scientific discovery.

Choosing a High-Quality Micropipette
When selecting a micropipette, consider:
- Brand Reputation: Opt for trusted manufacturers like Uma Scientific and Labolit, known for quality and affordability.
- Volume Range: Choose a model that suits your experimental needs.
- Ergonomics: Select lightweight, user-friendly designs.
- Calibration Standards: Ensure compliance with ISO .
- Budget: Indian brands offer cost-effective options without compromising performance.
Both Uma Scientific and Labolit provide a wide range of micropipettes, available across India. Contact them at +91 7347707507 for inquiries.
Conclusion
Mastering the use of a micropipette is a fundamental skill for anyone working in a laboratory. By following the steps outlined in this guide—selecting the right pipette, setting the volume, attaching tips, aspirating and dispensing correctly, and maintaining the instrument—you can achieve accurate and reproducible results. Adopting best practices, such as using sterile tips, calibrating regularly, and handling the pipette with care, ensures optimal performance and safety.
Brands like Uma Scientific and Labolit, India’s leading micropipette manufacturers, offer high-quality, low-cost solutions for laboratories worldwide. Whether you’re conducting cutting-edge research or routine diagnostics, their micropipettes empower you to work with precision and confidence. For more information or to purchase a micropipette, reach out to Uma Scientific or Labolit at +91 7347707507.
With practice and attention to detail, you’ll become proficient in using micropipettes, unlocking their full potential in your scientific endeavors.
- How to use a micropipette
- Micropipette guide for beginners
- Micropipette instructions step by step
- Micropipette usage tutorial
- Micropipette techniques and best practices
- Proper micropipette handling
- Using a micropipette correctly
- Micropipette step-by-step guide
- Micropipette calibration and maintenance
- Micropipette safety tips
- Accurate micropipetting methods
- Uma Scientific micropipette
- Labolit micropipette India
- Top micropipette brand India
- Buy micropipette in India

✅ Secondary Keyword Phrases (Supporting Content):
- Single-channel vs multi-channel micropipette
- Fixed volume vs variable volume micropipette
- Electronic micropipette usage
- What is a micropipette
- Types of micropipettes
- P10, P20, P100, P200, P1000 micropipette uses
- Pipetting techniques (forward/reverse)
- Micropipette tip compatibility
- Preventing pipetting contamination
- Sterile pipette tips
- Filter tips for PCR
- Viscous liquid pipetting tips
- Pipetting error troubleshooting
- Air bubbles in micropipette
- Autoclavable micropipettes
- ISO 8655 calibration micropipette
- Micropipette maintenance checklist
✅ Location-Based & Brand-Driven Keywords (Commercial & SEO):
- Micropipette manufacturer in India
- Best micropipette brand in India
- Uma Scientific micropipette distributor
- Micropipette suppliers in Delhi, Mumbai, Bangalore, etc.
- Affordable micropipette for lab use
- Indian micropipette brands
- Micropipette customer support India +91 7347707507
- Lab equipment Uma Scientific
- Uma Scientific vs Labolit micropipette

Micropipette Manufacturer in Andhra Pradesh – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Arunachal Pradesh – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Assam – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Bihar – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Chhattisgarh – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Goa – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Gujarat – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Haryana – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Himachal Pradesh – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Jharkhand – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Karnataka – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Kerala – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Madhya Pradesh – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Maharashtra – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Manipur – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Meghalaya – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Mizoram – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Nagaland – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Odisha – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Punjab – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Rajasthan – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Sikkim – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Tamil Nadu – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Telangana – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Tripura – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Uttar Pradesh – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Uttarakhand – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in West Bengal – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Andaman and Nicobar Islands – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Chandigarh – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Dadra and Nagar Haveli and Daman and Diu – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Delhi – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Jammu and Kashmir – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Ladakh – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Lakshadweep – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific
Micropipette Manufacturer in Puducherry – Best Quality Top Brand Uma Scientific




Craftnexgen Infotech
very good